by Pasquale Pirozzi, Associate Manager at Excellence Innovation
In 2024, the global artificial intelligence market was valued at $279.22 billion, and is projected to reach $1,811.75 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 35.9% between 2025 and 2030. Driving this growth are ongoing research and innovation efforts led by major tech players, which are accelerating the adoption of advanced solutions across various industries including automotive, healthcare, retail, finance, and manufacturing.
To remain competitive, companies now need project managers who can understand and integrate this technological evolution into decision-making and operational processes. It’s no longer just about adapting to new technologies — it’s about recognizing and leveraging artificial intelligence as a strategic lever to drive innovation and generate value.
In this evolving economic and technological landscape, project managers are called upon to determine when and how to adopt AI effectively in order to maintain a competitive edge.
Generative artificial intelligence is emerging as a transformative force capable of redefining traditional project management paradigms. Recent data shows that 21% of respondents in a Project Management Institute (PMI) survey already use AI tools frequently in their daily project management activities, leveraging these technologies to optimize operations and decision-making.
Beyond the frequent users, a growing number of professionals are experimenting with AI tools occasionally, suggesting an adoption curve that is set to rise in the coming years.
The same PMI study reveals that 82% of senior project managers believe that artificial intelligence will have a significant impact on project management strategies in the near future. The evidence is clear: AI should not be seen only as an operational tool, but as a strategic asset for driving organizational evolution.
How Generative AI Applies to Project Management
To maximize the transformative potential of generative AI tools, it’s essential to understand how this technology can be strategically applied within project management. The analytical framework developed by PMI researchers proposes evaluating project activities along two dimensions:
- the complexity of the activity;
- the degree of human intervention required.
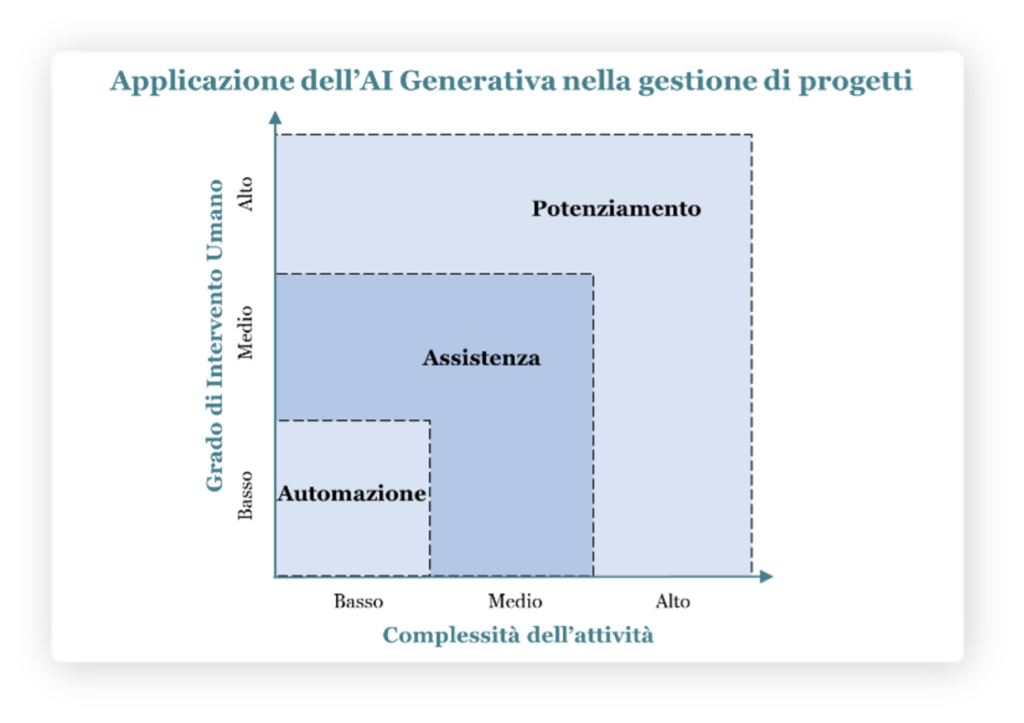
This chart highlights how AI adoption varies based on task complexity and the level of human input. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for identifying opportunities to improve project management processes and fully leverage AI potential. Each quadrant of the chart is now examined to understand the real-world applications of AI in project management.
Automation: Low Complexity, Low Human Input
In tasks with low complexity and minimal human input, AI manages repetitive, standardized, and low-value activities. The goal is to achieve operational efficiency.
Examples include:
- Automated report and financial analysis generation – AI tools compile and generate comprehensive reports detailing project status, financial metrics, and critical KPIs, freeing managers from hours of admin work.
- Smart auto-population in management tools – Automating updates and status inputs reduces manual data entry, minimizes errors, and improves data accuracy.
- Predictive resource optimization – AI analyzes project timelines, resource usage patterns, and contextual variables to automatically optimize activity planning and resource allocation.
- Intelligent quality control – Continuous monitoring of deliverables, automatic anomaly detection, and proactive waste management using machine learning algorithms.
Assistance: Medium Complexity, Medium Human Input
For medium-complexity activities where human oversight remains key, generative AI offers intelligent assistance to enhance decision-making and reduce cognitive load.
Use cases include:
- Assisted generation of strategic documentation – AI drafts initial versions of key documents (project plans, charters, technical specs) for managers to refine.
- Predictive risk analysis – AI uses historical data, market patterns, and predictive analytics to identify potential future risks and suggest proactive mitigation strategies.
- Advanced market intelligence – AI analyzes large datasets to extract trends, customer insights, and competitive opportunities for strategic decision-making.
- Smart project monitoring – Continuous analysis of project metrics versus performance benchmarks, with automatic alerts when values deviate from optimal thresholds.
Empowerment: High Complexity, High Human Input
In highly complex scenarios requiring strategic decision-making and deep data analysis, generative AI enhances human capabilities by providing advanced insights and predictive scenarios.
Examples include:
- Advanced scenario modeling – AI generates sophisticated simulations of multiple project scenarios, helping managers explore strategic implications and make better decisions in uncertainty.
- Facilitation of complex decision-making – AI integrates data from multiple sources to deliver insights supporting high-level strategic choices.
- Development of robust business cases – Detailed data analysis to build persuasive business cases that incorporate financial forecasts, risk assessments, and strategic evaluations.
This classification helps organizations understand where and how to integrate generative AI into their processes through a gradual, strategic approach that considers both task nature and human involvement.
Conclusion
With the AI market expected to reach $1.8 trillion by 2030 and economic impacts in the trillions, project managers are at the heart of a transformation that will redefine their profession. In a world increasingly driven by data and innovation, challenges abound — from technical integration to team readiness — but they also present an opportunity to reinforce the strategic leadership role of the project manager.
The most common mistake? Believing that AI can replace the project manager.
AI should be seen as the co-pilot: a technology that amplifies human value by eliminating routine and empowering strategic impact.
